Old Release
This documentation relates to an old version of DSpace, version 4.x. Looking for another version? See all documentation.
This DSpace release is end-of-life and is no longer supported.
What is DSpace Discovery
The Discovery Module enables faceted searching & browsing for your repository.
Although these techniques are new in DSpace, they might feel familiar from other platforms like Aquabrowser or Amazon, where facets help you to select the right product according to facets like price and brand. DSpace Discovery offers very powerful browse and search configurations that were only possible with code customization in the past.
Watch the DSpace Discovery introduction video
Since DSpace 4.0 Discovery is the default Search and Browse infrastructure for both XMLUI and JSPUI.
What is a Sidebar Facet
From the user perspective, faceted search (also called faceted navigation, guided navigation, or parametric search) breaks up search results into multiple categories, typically showing counts for each, and allows the user to "drill down" or further restrict their search results based on those facets.
When you have successfully enabled Discovery in your DSpace, you will notice that the different enabled facets are visualized in a "Discover" section in your sidebar, by default, right below the Browse options.
In this example, there are 3 Sidebar Facets, Author, Subject and Date Issued. It's important to know that multiple metadata fields can be included in one facet. For example, the Author facet above includes values from both dc.contributor.author as well as dc.creator.
Another important property of Sidebar Facets is that their contents are automatically updated to the context of the page. On collection homepages or community homepages it will include information about the items included in that particular collection or community.
What is a Search Filter
In a standard search operation, a user specifies his complete query prior to launching the operation. If the results are not satisfactory, the user starts over again with a (slightly) altered query.
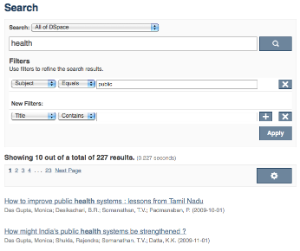
In a faceted search, a user can modify the list of displayed search results by specifying additional "filters" that will be applied on the list of search results. In DSpace, a filter is a contain condition applied to specific facets. In the example below, a user started with the search term "health", which yielded 500 results. After applying the filter "public" on the facet "Subject", only 227 results remain. Each time a user selects a sidebar facet it will be added as a filter. Active filters can be altered or removed in the 'filters' section of the search interface.
Another example: Using the standard search, a user would search for something like [wetland + "dc.author=Mitsch, William J" + dc.subject="water quality" ]. With filtered search, they can start by searching for [wetland ], and then filter the results by the other attributes, author and subject.
Discovery Changelist
DSpace 4.0
General improvements:
- Browse interfaces now also use Discovery index (rather than the legacy Lucene index)
- "Did you means" spell check aid for search
DSpace 3.0
General improvements:
- Hierarchical facets sidebar facets
- Improved & more intuitive user interface
- Access Rights Awareness (enabled by default). Access restricted or embargoed content is hidden from anonymous search/browse.
- Authority control & variants awareness (homonyms are shown separately in a facet if they have different authority ID). All variant forms as recognized by the authority framework are indexed. See Authority Framework
XMLUI-only:
- Hit highlighting and search snippets support
- "More like this" (related items)
Bugfixes and other changes
- Auto-complete functionality has been removed in XMLUI from search queries due to performance issues. JSPUI still supports auto-complete functionality without performance issues.
DSpace 1.8
- Configuration moved from dspace.cfg into
config/modules/discovery.cfgandconfig/spring/api/discovery.xml - Individual communities and collections can have their own Discovery configuration.
- Tokenization for Auto-complete values (see SearchFilter)
- Alphanumeric sorting for Sidebarfacets
- Possibility to avoid indexation of specific metadata fields.
- Grouping of multiple metadata fields under the same SidebarFacet
DSpace 1.7
- Sidebar browse facets that can be configured to use contents from any metadata field
- Dynamically generated timespans for dates
- Customizable "recent submissions" view on the repository homepage, collection and community pages
- Hit highlighting & search snippets
Enabling Discovery
Because Discovery was adopted as the default infrastructure for search and browse in DSpace 4, no manual steps are required to enable Discovery. If you want to enable Discovery on older versions of DSpace, please refer to the DSpace documentation for that particular version.
Configuration files
The configuration for discovery is located in 2 separate files.
- General settings: The
discovery.cfgfile located in the[dspace-install-dir]/config/modules directory. - User Interface Configuration: The
discovery.xmlfile is located in[dspace-install-dir]/config/spring/api/directory.
General Discovery settings (config/modules/discovery.cfg)
The discovery.cfg file is located in the [dspace-install-dir]/config/modules directory and contains following properties:
Property: | search.server |
Example Value: |
|
Informational Note: | Discovery relies on a Solr index for storage and retrieval of its information. This parameter determines the location of the Solr index. |
Property: | index.ignore |
Example Value: |
|
Informational Note: | By default, Discovery will include all of the DSpace metadata in its search index. In cases where specific metadata is confidential, repository managers can include those fields by adding them to this comma separated list. |
| Property: | index.authority.ignore[.field] |
| Example Value: |
|
| Informational Note: | By default, Discovery will use the authority information in the metadata to disambiguate homonyms. Setting this property to false will make the indexing process the same as the metadata doesn't include authority information. The configuration can be different on a field (<schema>.<element>.<qualifier>) basis, the property without field set the default value. |
| Property: | index.authority.ignore-prefered[.field] |
| Example Value: |
|
| Informational Note: | By default, Discovery will use the authority information in the metadata to query the authority for the prefered label. Setting this property to false will make the indexing process the same as the metadata doesn't include authority information (i.e. the prefered form is the one recorded in the metadata value). The configuration can be different on a field (<schema>.<element>.<qualifier>) basis, the property without field set the default value. If the authority is a remote service, disabling this feature can greatly improve performance. |
| Property: | index.authority.ignore-variants[.field] |
| Example Value: |
|
| Informational Note: | By default, Discovery will use the authority information in the metadata to query the authority for variants. Setting this property to false will make the indexing process the same, as the metadata doesn't include authority information. The configuration can be different on a per-field (<schema>.<element>.<qualifier>) basis, the property without field set the default value. If authority is a remote service, disabling this feature can greatly improve performance. |
Modifying the Discovery User Interface (config/spring/api/discovery.xml)
The discovery.xml file is located in the [dspace-install-dir]/config/spring/api directory.
Structure Summary
This file is in XML format, you should be familiar with XML before editing this file. The configurations are organized together in beans, depending on the purpose these properties are used for.
This purpose can be derived from the class of the beans. Here's a short summary of classes you will encounter throughout the file and what the corresponding properties in the bean are used for.
Download the configuration file and review it together with the following parameters
Class: | DiscoveryConfigurationService |
Purpose: | Defines the mapping between separate Discovery configurations and individual collections/communities |
Default: | All communities, collections and the homepage (key=default) are mapped to defaultConfiguration |
Class: | DiscoveryConfiguration |
Purpose: | Groups configurations for sidebar facets, search filters, search sort options and recent submissions |
Default: | There is one configuration by default called defaultConfiguration |
Class: | DiscoverySearchFilter |
Purpose: | Defines that specific metadata fields should be enabled as a search filter |
Default: | dc.title, dc.contributor.author, dc.creator, dc.subject.* and dc.date.issued are defined as search filters |
Class: | DiscoverySearchFilterFacet |
Purpose: | Defines which metadata fields should be offered as a contextual sidebar browse options, each of these facets has also got to be a search filter |
Default: | dc.contributor.author, dc.creator, dc.subject.* and dc.date.issued |
Class: | HierarchicalSidebarFacetConfiguration |
Purpose: | Defines which metadata fields contain hierarchical data and should be offered as a contextual sidebar option |
Class: | DiscoverySortConfiguration |
Purpose: | Further specifies the sort options to which a DiscoveryConfiguration refers |
Default: | dc.title and dc.date.issued are defined as alternatives for sorting, other than Relevance (hard-coded) |
Class: | DiscoveryHitHighlightingConfiguration |
Purpose: | Defines which metadata fields can contain hit highlighting & search snippets |
Default: | dc.title, dc.contributor.author, dc.subject, dc.description.abstract & full text from text files. |
Default settings
In addition to the summarized descriptions of the default values, following details help you to better understand these defaults. If you haven't already done so, download the configuration file and review it together with the following parameters.
The file contains one default configuration that defines following sidebar facets, search filters, sort fields and recent submissions display:
- Sidebar facets
- searchFilterAuthor: groups the metadata fields dc.contributor.author & dc.creator with a facet limit of 10, sorted by occurrence count
- searchFilterSubject: groups all subject metadata fields (dc.subject.*) with a facet limit of 10, sorted by occurrence count
- searchFilterIssued: contains the dc.date.issued metadata field, which is identified with the type "date" and sorted by specific date values
- Search filters
- searchFilterTitle: contains the dc.title metadata field
- searchFilterAuthor: contains the dc.contributor.author & dc.creator metadata fields
- searchFilterSubject: contains the dc.subject.* metadata fields
- searchFilterIssued: contains the dc.date.issued metadata field with the type "date"
- Sort fields
- sortTitle: contains the dc.title metadata field
- sortDateIssued: contains the dc.date.issued metadata field, this sort has the type date configured.
- defaultFilterQueries
- The default configuration contains no defaultFilterQueries
- The default filter queries are disabled by default but there is an example in the default configuration in comments which allows discovery to only return items (as opposed to also communities/collections).
- Recent Submissions
- The recent submissions are sorted by dc.date. accessioned which is a date and a maximum number of 5 recent submissions are displayed.
- Hit highlighting
- The fields dc.title, dc.contributor.author & dc.subject can contain hit highlighting.
- The dc.description.abstract & full text field are used to render search snippets.
Many of the properties contain lists that use references to point to the configuration elements. This way a certain configuration type can be used in multiple discovery configurations so there is no need to duplicate them.
Search filters & sidebar facets Customization
This section explains the properties for search filters & sidebar facets. Each sidebar facet must occur in the reference list of the search filters. Below is an example configuration of a search filter that is not used as a sidebar facet.
<bean id="searchFilterTitle" class="org.dspace.discovery.configuration.DiscoverySearchFilter">
<property name="indexFieldName" value="title"/>
<property name="metadataFields">
<list>
<value>dc.title</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
The id & class attributes are mandatory for this type of bean. The properties that it contains are discussed below.
- indexFieldName (Required): A unique search filter name, the metadata will be indexed in Solr under this field name.
- metadataFields (Required): A list of the metadata fields that need to be included in the facet.
Sidebar facets extend the search filter and add some extra properties to it, below is an example of a search filter that is also used as a sidebar facet.
<bean id="searchFilterAuthor" class="org.dspace.discovery.configuration.SidebarFacetConfiguration">
<property name="indexFieldName" value="author"/>
<property name="metadataFields">
<list>
<value>dc.contributor.author</value>
<value>dc.creator</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="facetLimit" value="10"/>
<property name="sortOrder" value="COUNT"/>
<property name="type" value="text"/>
</bean>
Note that the class has changed from DiscoverySearchFilter to SidebarFacetConfiguration this is needed to support the extra properties.
- facetLimit (optional): The maximum number of values to be shown. This property is optional, if none is specified the default value "10" will be used. If the filter has the type date, this property will not be used since dates are automatically grouped together.
- sortOrder (optional):The sort order for the sidebar facets, it can either be COUNT or VALUE. The default value is COUNT.
- COUNT Facets will be sorted by the amount of times they appear in the repository
- VALUE Facets will be sorted alphabetically
- type(optional): the type of the sidebar facet it can either be "date" or "text", "text" is the default value.
- text: The facets will be treated as is
- date: Only the year will be stored in the Solr index. These years are automatically displayed in ranges that get smaller when you select one.
Hierarchical (taxonomies based) sidebar facets
Discovery supports specialized drill down in hierarchically structured metadata fields. For this drill down to work, the metadata in the field for which you enable this must be composed out of terms, divided by a splitter. For example, you could have a dc.subject.taxonomy field in which you keep metadata like "CARTOGRAPHY::PHOTOGRAMMETRY", in which Cartography and Photogrammetry are both terms, divided by the splitter "::". The sidebar will only display the top level facets, when clicking on view more all the facet options will be displayed.
<bean id="searchFilterSubject" class="org.dspace.discovery.configuration.HierarchicalSidebarFacetConfiguration">
<property name="indexFieldName" value="subject"/>
<property name="metadataFields">
<list>
<value>dc.subject</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="sortOrder" value="COUNT"/>
<property name="splitter" value="::"/>
<property name="skipFirstNodeLevel" value="false"/>
</bean>
Note that the class has changed from SidebarFacetConfiguration to HierarchicalSidebarFacetConfiguration this is needed to support the extra properties.
- splitter (required): The splitter used to split up the separate nodes
- skipFirstNodeLevel (optional): Whether or not to show the root node level. For some hierarchical data there is a single root node. In most cases it doesn't need to be shown since it isn't relevant. This property is true by default.
Sort option customization for search results
This section explains the properties of an individual SortConfiguration, like sortTitle and sortDateIssued from the default configuration. In order to create custom sort options, you can either modify specific properties of those that already exist or create a totally new one from scratch.
Here's what the sortTitle SortConfiguration looks like:
<bean id="sortTitle" class="org.dspace.discovery.configuration.DiscoverySortFieldConfiguration">
<property name="metadataField" value="dc.title"/>
<property name="type" value="text"/>
</bean>
The id & class attributes are mandatory for this type of bean. The properties that it contains are discussed below.
- metadataField (Required): The metadata field indicating the sort values
- type (optional): the type of the sort option can either be date or text, if none is defined text will be used.
DiscoveryConfiguration
The DiscoveryConfiguration Groups configurations for sidebar facets, search filters, search sort options and recent submissions. If you want to show the same sidebar facets, use the same search filters, search options and recent submissions everywhere in your repository, you will only need one DiscoveryConfiguration and you might as well just edit the defaultConfiguration.
The DiscoveryConfiguration makes it very easy to use custom sidebar facets, search filters, ... on specific communities or collection homepage. This is particularly useful if your collections are heterogeneous. For example, in a collection with conference papers, you might want to offer a sidebar facet for conference date, which might be more relevant than the actual issued date of the proceedings. In a collection with papers, you might want to offer a facet for funding bodies or publisher, while these fields are irrelevant for items like learning objects.
A DiscoveryConfiguration consists out of five parts
- The list of applicable sidebarFacets
- The list of applicable searchFilters
- The list of applicable searchSortFields
- Any default filter queries (optional)
- The configuration for the Recent submissions display
Configuring lists of sidebarFacets and searchFilters
After modifying sidebarFacets and searchFilters, don't forget to reindex existing items by running [dspace]/bin/dspace index-discovery -b, otherwise the changes will not appear.
Below is an example of how one of these lists can be configured. It's important that each of the bean references corresponds to the exact name of the earlier defined facets, filters or sort options.
Each sidebar facet must also occur in the list of the search filters.
<property name="sidebarFacets">
<list>
<ref bean="sidebarFacetAuthor" />
<ref bean="sidebarFacetSubject" />
<ref bean="sidebarFacetDateIssued" />
</list>
</property>
Configuring and customizing search sort fields
The search sort field configuration block contains the available sort fields and the possibility to configure a default sort field and sort order.
Below is an example of the sort configuration.
<property name="searchSortConfiguration">
<bean class="org.dspace.discovery.configuration.DiscoverySortConfiguration">
<!--<property name="defaultSort" ref="sortDateIssued"/>-->
<!--DefaultSortOrder can either be desc or asc (desc is default)-->
<property name="defaultSortOrder" value="desc"/>
<property name="sortFields">
<list>
<ref bean="sortTitle" />
<ref bean="sortDateIssued" />
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</property>
The property name & the bean class are mandatory. The property field names are discusses below.
- defaultSort (optional): The default field on which the search results will be sorted, this must be a reference to an existing search sort field bean. If none is given relevance will be the default. Sorting according to the internal relevance algorithm is always available, even though it's not explicitly mentioned in the sortFields section.
- defaultSortOrder (optional): The default sort order can either be asc or desc.
- sortFields (mandatory): The list of available sort options, each element in this list must link to an existing sort field configuration bean.
Adding default filter queries (OPTIONAL)
Default filter queries are applied on all search operations & sidebarfacet clicks. One useful application of default filter queries is ensuring that all returned results are items. As a result, subcommunities and collections that are returned as results of the search operation, are filtered out.
Similar to the lists above, the default filter queries are defined as a list. They are optional.
<property name="defaultFilterQueries">
<list>
<value>query1</value>
<value>query2</value>
</list>
</property>
This property contains a simple list which in turn contains the queries. Some examples of possible queries:
- search.resourcetype:2
- dc.subject:test
- dc.contributor.author: "Van de Velde, Kevin"
- ...
Access Rights Awareness
By default, when searching and browsing using Discovery, you will only see items that you have access to. So, your search/browse results may differ if you are logged into DSpace. This Access Rights Awareness feature ensures that anonymous users (and search engines) are not able to access information (both files and metadata) about embargoed or private items. It also provides you with more direct control over who can see individual items within your DSpace.
How does Access Rights Awareness work?
Access Rights Awareness checks the "READ" access on the Item.
If the "Anonymous" group has "READ" access on the Item, then anonymous/public users will be able to view that Item's metadata and locate that Item via DSpace's search/browse system. In addition, search engines will also be able to index that Item's metadata. However, even with Anonymous READ set at the Item-level, you may still choose to access-restrict the downloading/viewing of files within the Item. To do so, you would restrict "READ" access on individual Bitstream(s) attached to the Item.
If the "Anonymous" group does NOT have "READ" access on the Item, then anonymous users will never see that Item appear within their search/browse results (essentially the Item is "invisible" to them). In addition, that Item will be invisible to search engines, so it will never be indexed by them. However, any users who have been given READ access will be able to find/locate the item after logging into DSpace. For example, if a "Staff" group was provided "READ" access on the Item, then members of that "Staff" group would be able to locate the item via search/browse after logging into DSpace.
How can I disable Access Rights Awareness?
If you prefer to allow all access-restricted or embargoed Items to be findable within your DSpace, you can choose to turn off Access Rights Awareness. However, please be aware that this means that restricting "READ" access on an Item will not really do anything – the Item metadata will be available to the public no matter what group(s) were given READ access on that Item.
This feature can be switched off by going to the [dspace.dir]/config/spring/api/discovery.xml file & commenting out the bean & the alias shown below.
<bean class="org.dspace.discovery.SolrServiceResourceRestrictionPlugin" id="solrServiceResourceIndexPlugin"/> <alias name="solrServiceResourceIndexPlugin" alias="org.dspace.discovery.SolrServiceResourceRestrictionPlugin"/>
The Browse Engine only supports the "Access Rights Awareness" if the Solr/Discovery backend is enabled (see Defining the Storage of the Browse Data). However, it is enabled by default for DSpace 3.x and above.
Access Rights Awareness - technical details
The DSpaceObject class has an updateLastModified() method which will be triggered each time an authorization policy changes. This method is only implemented in the item class where the last_modified timestamp will be updated and a modify event will be fired. By doing this we ensure that the discovery consumer is called and the item is reindexed. Since this feature can be switched off a separate plugin has been created: the SolrServiceResourceRestrictionPlugin. Whenever we reindex a DSpace object all the read rights will be stored in the read field. We make a distinction between groups and users by adding a 'g' prefix for groups and the 'e' prefix for epersons.
When searching in discovery all the groups the user belongs to will be added as a filter query as well as the users identifier. If the user is an admin all items will be returned since an admin has read rights on everything.
Customizing the Recent Submissions display
This paragraph only applies to XMLUI. JSPUI relies on the Browse Engine to show "recent submissions". This requires that the Solr/Discovery backend is enabled (see Defining the Storage of the Browse Data).
The recent submissions configuration element contains all the configuration settings to display the list of recently submitted items on the home page or community/collection page. Because the recent submission configuration is in the discovery configuration block, it is possible to show 10 recently submitted items on the home page but 5 on the community/collection pages.
Below is an example configuration of the recent submissions.
<property name="recentSubmissionConfiguration">
<bean class="org.dspace.discovery.configuration.DiscoveryRecentSubmissionsConfiguration">
<property name="metadataSortField" value="dc.date.accessioned"/>
<property name="type" value="date"/>
<property name="max" value="5"/>
</bean>
</property>
The property name & the bean class are mandatory. The property field names are discusses below.
- metadataSortField (mandatory): The metadata field to sort on to retrieve the recent submissions
- max (mandatory): The maximum number of results to be displayed as recent submissions
- type (optional): the type of the search filter. It can either be date or text, if none is defined text will be used.
Customizing hit highlighting & search snippets
This paragraph only applies to XMLUI. JSPUI does not currently support "highlighting & search snippets".
The hit highlighting configuration element contains all settings necessary to display search snippets & enable hit highlighting.
Changes made to the configuration will not automatically be displayed in the user interface. By default, only the following fields are displayed: dc.title, dc.contributor.author, dc.creator, dc.contributor, dc.date.issued, dc.publisher, dc.description.abstract and fulltext.
If additional fields are required, look for the "itemSummaryList" template.
Below is an example configuration of hit highlighting.
<property name="hitHighlightingConfiguration">
<bean class="org.dspace.discovery.configuration.DiscoveryHitHighlightingConfiguration">
<property name="metadataFields">
<list>
<bean class="org.dspace.discovery.configuration.DiscoveryHitHighlightFieldConfiguration">
<property name="field" value="dc.title"/>
<property name="snippets" value="5"/>
</bean>
<bean class="org.dspace.discovery.configuration.DiscoveryHitHighlightFieldConfiguration">
<property name="field" value="dc.contributor.author"/>
<property name="snippets" value="5"/>
</bean>
<bean class="org.dspace.discovery.configuration.DiscoveryHitHighlightFieldConfiguration">
<property name="field" value="dc.subject"/>
<property name="snippets" value="5"/>
</bean>
<bean class="org.dspace.discovery.configuration.DiscoveryHitHighlightFieldConfiguration">
<property name="field" value="dc.description.abstract"/>
<property name="maxSize" value="250"/>
<property name="snippets" value="2"/>
</bean>
<bean class="org.dspace.discovery.configuration.DiscoveryHitHighlightFieldConfiguration">
<property name="field" value="fulltext"/>
<property name="maxSize" value="250"/>
<property name="snippets" value="2"/>
</bean>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</property>
The property name & the bean class are mandatory. The property field names are:
- field (mandatory): The metadata field to be highlighted (can also be
*if all the metadata fields should be highlighted). - maxSize (optional): Limit the number of characters displayed to only the relevant part (use metadata field as search snippet).
- snippets (optional): The maximum number of snippets that can be found in one metadata field.
Hit highlighting technical details
The org.dspace.discovery.DiscoveryQuery object has a setter & getter for the hit highlighting configuration set in Discovery configuration. If this configuration is given the resolveToSolrQuery method located in the org.dspace.discovery.SolrServiceImpl class will use the standard Solr highlighting feature (http://wiki.apache.org/solr/HighlightingParameters). The org.dspace.discovery.DiscoverResult class has a method to set the highlighted fields for each object & field.
The rendering of search results is no longer handled by the METS format but uses a special type of list named "TYPE_DSO_LIST". Each metadata field (& fulltext if configured) is added in the DRI and IF the field contains hit higlighting the Java code will split up the string & add DRI highlights to the list. The XSL for the themes also contains special rendering XSL for the DRI; for Mirage, the changes are located in the discovery.xsl file. For themes using the old themes based on structural.xsl, look for the template matching "dri:list[@type='dsolist']".
"More like this" configuration
This paragraph only apply to XMLUI. The JSPUI does not currently support the "More like this" feature.
The "more like this"-configuration element contains all the settings for displaying related items on an item display page.
Below is an example of the "more like this" configuration.
<property name="moreLikeThisConfiguration">
<bean class="org.dspace.discovery.configuration.DiscoveryMoreLikeThisConfiguration">
<property name="similarityMetadataFields">
<list>
<value>dc.title</value>
<value>dc.contributor.author</value>
<value>dc.creator</value>
<value>dc.subject</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--The minimum number of matching terms across the metadata fields above before an item is found as related -->
<property name="minTermFrequency" value="5"/>
<!--The maximum number of related items displayed-->
<property name="max" value="3"/>
<!--The minimum word length below which words will be ignored-->
<property name="minWordLength" value="5"/>
</bean>
</property>
The property name & the bean class are mandatory. The property field names are discussed below.
- similarityMetadataFields: the metadata fields checked for similarity
- minTermFrequency: The minimum number of matching terms accross the metadata fields above before an item is found as related
- max: The maximum number of related items displayed
- minWordLength: The minimum word length below which words will be ignored
"More like this" technical details
The org.dspace.discovery.SearchService object has received a getRelatedItems() method. This method requires an item & the more-like-this configuration bean from above. This method is implemented in the org.dspace.discovery.SolrServiceImpl which uses the item as a query & uses the default Solr parameters for more-like-this to pass the bean configuration to solr (https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/solr/MoreLikeThis). The result will be a list of items or if none found an empty list. The rendering of this list is handled in the org.dspace.app.xmlui.aspect.discovery.RelatedItems class.
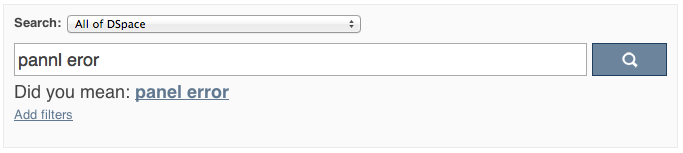
"Did you mean" spellcheck aid for search configuration
DSpace 4 introduces the use of SOLR's SpellCheckComponent as an aid for search. When a user's search does not return any hits, the user is presented with a suggestion for an alternative search query.
The feature currently only one line of configuration to discovery.xml. Changing the value from true to false will disable the feature.
<property name="spellCheckEnabled" value="true" />
"Did you mean" spellcheck aid for search technical details
Similar to the More like this configuration, SOLR's spell check component is used with default configuration values. Any of these values can be overridden in the solrconfig.xml file located in dspace/solr/search/conf/. Following links provide more information about the SOLR SpellCheckComponent:
http://wiki.apache.org/solr/SpellCheckComponent
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/solr/Spell+Checking
Discovery Solr Index Maintenance
Command used: |
|
Java class: | org.dspace.discovery.IndexClient |
Arguments (short and long forms): | Description |
| called without any options, will update/clean an existing index |
| (re)build index, wiping out current one if it exists |
| clean existing index removing any documents that no longer exist in the db |
| if updating existing index, force each handle to be reindexed even if uptodate |
| print this help message |
| optimize search core |
| remove an Item, Collection or Community from index based on its handle |
| -s | Rebuild the spellchecker, can be combined with -b and -f. |
Routine Discovery Solr Index Maintenance
It is strongly recommended to run maintenance on the Discovery Solr index daily (from crontab or your system's scheduler), to prevent your servlet container from running out of memory:
[dspace]/bin/dspace index-discovery -o
Advanced Solr Configuration
Discovery is built as an application layer on top of the Solr open source enterprise search server. Therefore, Solr configuration can be applied to the Solr cores that are shipped with DSpace.
The DSpace Solr instance itself now runs two cores. One for collection DSpace Solr based "statistics", the other for Discovery Solr based "search".
solr
├── search
│ ├── conf
│ │ ├── admin-extra.html
│ │ ├── elevate.xml
│ │ ├── protwords.txt
│ │ ├── schema.xml
│ │ ├── scripts.conf
│ │ ├── solrconfig.xml
│ │ ├── spellings.txt
│ │ ├── stopwords.txt
│ │ ├── synonyms.txt
│ │ └── xslt
│ │ ├── DRI.xsl
│ │ ├── example.xsl
│ │ ├── example_atom.xsl
│ │ ├── example_rss.xsl
│ │ └── luke.xsl
│ └── conf2
├── solr.xml
└── statistics
└── conf
├── admin-extra.html
├── elevate.xml
├── protwords.txt
├── schema.xml
├── scripts.conf
├── solrconfig.xml
├── spellings.txt
├── stopwords.txt
├── synonyms.txt
└── xslt
├── example.xsl
├── example_atom.xsl
├── example_rss.xsl
└── luke.xsl

2 Comments
Alvin Hutchinson
I think the last section where the solr/search/conf/schema.xml file is mentioned should include the notation that to change boolean (search) operator from 'OR' to 'AND' the schema.xml file has to be edited.
Ivan Masár
You can find info on advanced usage of Solr here:
https://wiki.duraspace.org/display/DSPACE/Solr