Old Release
This documentation relates to an old version of DSpace, version 5.x. Looking for another version? See all documentation.
Support for DSpace 5 ended on January 1, 2023. See Support for DSpace 5 and 6 is ending in 2023
WORK IN PROGRESS
Introduction
The ORCID integration adds ORCID compatibility to the existing solutions for Authority control in DSpace. String names of authors are still being stored in DSpace metadata. The authority key field is leveraged to store a uniquely generated internal ID that links the author to more extended metadata, including the ORCID ID and alternative author names.
This extended metadata is stored and managed in a dedicated SOLR index, the DSpace authority cache.
Timeline
This functionality is still under development and is scheduled to be contributed as part of the DSpace 5 release.
Checklist: this is when you're done
Use case and high level benefits
The vision behind this project consists of the following two aspects:
Lowering the threshold to adopt ORCID for the members of the DSpace community
ORCID’s API has enabled developers across the globe to build points of integration between ORCID and third party applications. Up until today, this meant that members of the DSpace community were still required to implement front-end and back-end modifications to the DSpace source code in order to leverage these APIs. As DSpace aims to provide turnkey Institutional Repository functionality, the platform is expected to provide more functionality out of the box. Only an elite selection of members in the DSpace community has software development resources readily available to implement this kind of functionality. By contributing a solution directly to the core DSpace codebase, this threshold to adopt ORCID functionality in DSpace repositories is effectively lowered. The ultimate goal is to allow easy adoption of ORCID without customization of the DSpace software, by allowing repository administrators to enable or disable functionality by means of user friendly configuration.
Address generic use cases with appealing end user functionality
This proposal aims to provide user friendly features for both repository administrators as well as non- technical end users of the system. The addition of ORCID functionality to DSpace should not come at the cost of making the system more difficult for administrators and end users to use. Scope With this vision in mind, the project partners wanted to tackle the first phases for repository managers of existing DSpace repositories: ensuring that ORCIDs are properly associated with new works entering the system, as well as providing functionality to efficiently batch-update content already existing in the system, with unambiguous author identity information.
Enabling the ORCID authority control
If you wish to enable this feature, some changes are required to the dspace.cfg file. The first step is to activate the authority as a valid option for authority control, this is done by adding/setting an additional plugin in the plugin.named.org.dspace.content.authority.ChoiceAuthority property. An example of this can be found below.
plugin.named.org.dspace.content.authority.ChoiceAuthority = \
org.dspace.content.authority.SolrAuthority = SolrAuthorAuthority
The feature relies on the following configuration parameters in dspace.cfg. To activate the default settings it suffices to remove the comment hashes ("#") for the following lines. See the section at the bottom of this page what these parameters mean exactly and how you can tweak the configuration.
solr.authority.server=${solr.server}/authority
choices.plugin.dc.contributor.author = SolrAuthorAuthority
choices.presentation.dc.contributor.author = authorLookup
authority.controlled.dc.contributor.author = true
authority.author.indexer.field.1=dc.contributor.author
The final part of configuration is to add the authority consumer in front of the list of event consumers. Add "authority" in front of the list as displayed below.
event.dispatcher.default.consumers = authority, versioning, discovery, eperson, harvester
Technical Implementation Details
JSPUI Support
In DSpace 5.0 the functionality only includes user interface functionality for the DSpace XML User Interface.
XMLUI Theme Support
In DSpace 5.0 the functionality only adds support for the XMLUI Mirage and Mirage 2 themes. Older XMLUI themes including Kubrick, Reference and Classic are currently unsupported.
Submission of new DSpace items - Author lookup
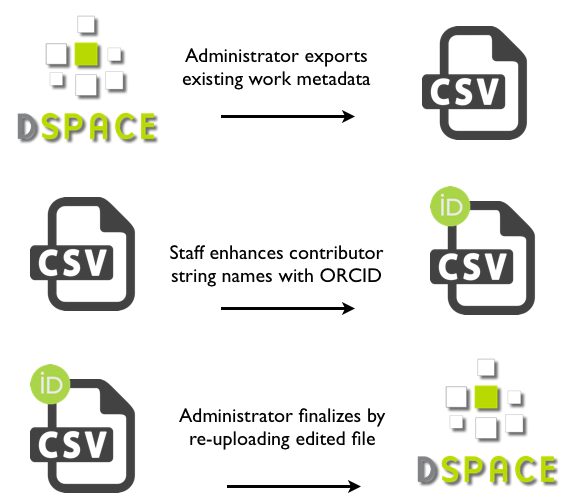
Editing existing items using Batch CSV Editing
Storage of related metadata
ORCID authorities not only link a digital identifier to a name. It regroups a load of metadata going from alternative names and email addresses to keywords about their works and much more. In order to avoid querying the ORCID web services every time for some information, all these related metadata is gathered in a "metadata authority cache" that DSpace can access directly.
In practice the cache is provided by an apache solr server. When a look-up is made and an author is chosen that is not yet in the cache, a record is created from an ORCID profile and added to the cache with the list of related metadata. The value of the Dublin Core metadata is based on the first and last name as they are set in the ORCID profile. The authority key for this value links directly to the solr document's id.
The information in the authority cache can be updated by running the following command line operation:
[dspace]/bin/dspace dsrun org.dspace.authority.UpdateAuthoritiesThis will iterate over every solr record currently in use, query the ORCID web service for the latest data and update the information in the cache. If configured, the script will also update the metadata of the items in the repository where applicable.
Configuration - wip
In the Enabling the ORCID authority control section, you have been told to add this block of configuration.
solr.authority.server=${solr.server}/authority
choices.plugin.dc.contributor.author = SolrAuthorAuthority
choices.presentation.dc.contributor.author = authorLookup
authority.controlled.dc.contributor.author = true
authority.author.indexer.field.1=dc.contributor.author
The ORCID Integration feature is an extension on the authority control in DSpace. Most of these properties are extensively explained on the Authority Control of Metadata Values documentation page. These will be revisited but first we cover the properties that have been newly added.
- The
solr.authority.serveris the url to the solr core. Usually this would be on thesolr.servernext to the oai, search and statistics cores. authority.author.indexer.field.1and the subsequent increments configure which fields the authority consumer indexes.
That's it for the novelties. Moving on to the generic authority control properties:
- With the
authority.controlledproperty every metadata field that needs to be authority controlled is configured. This involves every type of authority control, not only the fields for ORCID integration. - The
choices.pluginshould be configured for each metadata field under authority control. Setting the value on SolrAuthorAuthority tells DSpace to use the solr authority cache for this metadatafield, cfr. Storage of related metadata. - The
choices.presentionshould be configured for each metadata field as well. The traditional values for this property areselect|suggest|lookup. A new value,authorLookup, has been added to be used in combination with the SolrAuthorAuthority choices plugin. While the other values can still be used, the authorLookup provides a richer user interface in the form of a popup on the submission page. - More existing configuration properties are available but their values are independent of this feature and their default values are usually fine:
choices.closed,authority.required,authority.minconfidence
For the cache update script, one property can be set in config/modules/solrauthority.cfg:
auto-update-items = false | true
The default value for when the property is missing is false.
Changes to the configuration always require a server restart before they're in effect.