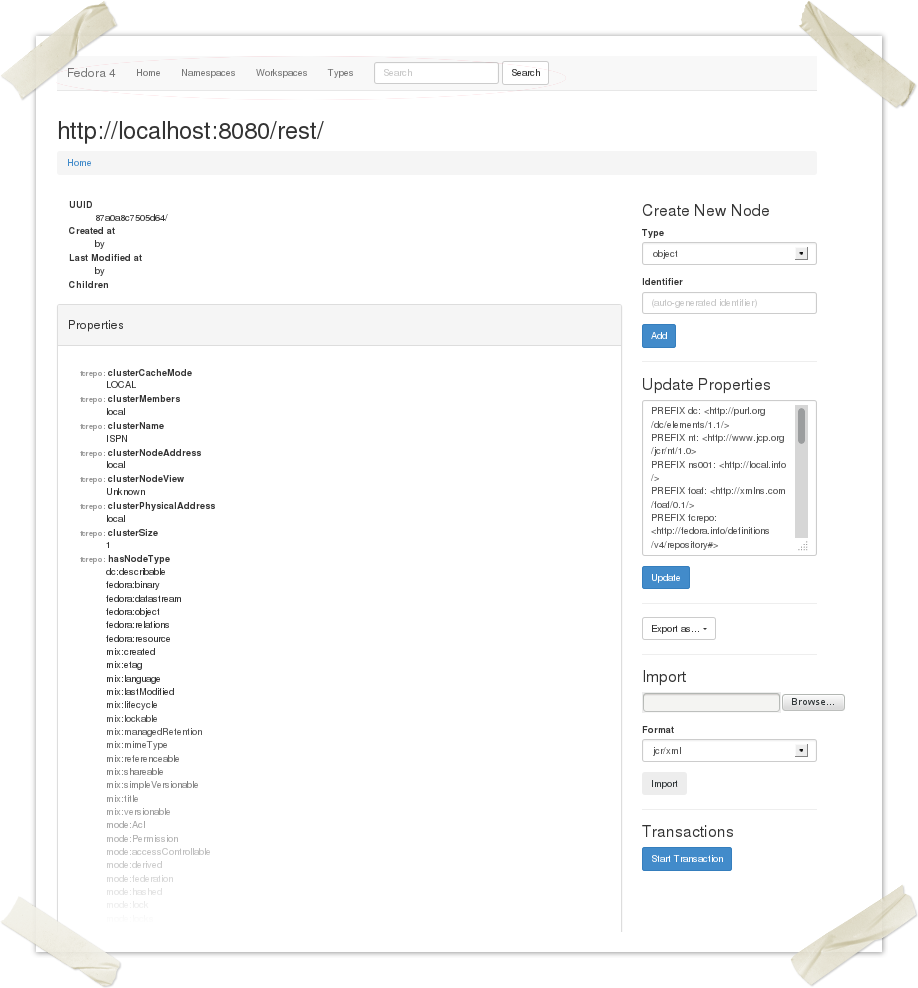
1 Object Title If a title (either http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#label or http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/title) is available, it is displayed here. If no title has been assigned, the resource URI is displayed in this location.
2 Object Path Fedora 4 is different from Fedora 3 in that there is an innate tree hierarchy to the repository rather than a flat hierarchy. The path (list of ancestors) for the viewed node is presented below the object title. Performance is expected to be better with a deeper hierarchy with fewer items per level as opposed to a shallower where each level has a larger number of siblings. The automatic ID (and path) generated is meant to optimize performance but you may use your own organizational strategy when creating objects and datastreams.
In this particular example, the object was created with a fully qualified name including a namespace and local name (separated by a colon). Fedora 4 does not require that identifeirs have namespaces, but if you wish to use them
3 Featured PropertiesVery basic metadata such as the UUID and modification/creation times and users are presented below the object path 4 Children
Any children that the node has will be listed and linked here. Like the subject node, if these children have recognized title metadata, that title will be presented here rather than their URI. 5 All Node Properties All properties of the node are presented here. Hover your mouse over the namespace prefix to see the full namespace.
6 Inlined Resources A subset of properties from the parent node, children nodes are presented below the properties for the subject node. Click on the grayed box to expand the list of properties or the label text to view that resource directly.
|